(PDF) The Role of HLA DQ2 and DQ8 in Dissecting CeliacLike Disease in Common Variable

Here's why: "HLA-DQ2 and HLA-DQ8 are the names of two genetic markers which are part of the immune system and are able to stick to the gluten proteins. Every person with celiac disease has at least one of these genetic markers. If your doctor is unsure as to whether or not you have celiac disease, s/he can perform a simple blood test to.
(PDF) Validation of a novel singledrop rapid HLADQ2/DQ8 typing method to identify subjects

Use. Aids in the diagnosis of celiac disease. The HLA DQ Association test provides genotyping for detection of HLA-DQ2 (DQA1*05:01 or 05:05 and DQB1*02:01 or 02:02) and HLA-DQ8 (DQB1*03:02). Patients with DQ2, half DQ2 and/or DQ8 are predisposed to celiac disease. A negative result essentially rules out celiac disease.
Expression of HLADQ2/8 transdimers on viraltransduced HEK293 cells.... Download Scientific

111, 112 Further, CeD patients neither expressing HLA-DQ2,5, HLA-DQ2.2 nor HLA-DQ8 were found to carry DQA1*05 on an HLA-DQ7 haplotype without carrying DQB1*02 112suggesting that HLA-DQ7 may be implicated in the pathogenesis. Although developing CeD in the absence of the HLA-DQ2.5, HLA-DQ2.2 or HLA-DQ8 allotypes remains rare, these findings
High rates of variation in HLADQ2/DQ8 testing for coeliac disease results from an RCPAQAP

Celiac disease is a genetic condition, which means you need to have certain genes to develop it and to be diagnosed with it. HLA-DQ2 is one of two main celiac disease genes, and it is the most common gene implicated in celiac disease (HLA-DQ8 is the other celiac gene). Most doctors believe you need at least one copy of either HLA-DQ2 or HLA-DQ8.
PPT HLA typing d isease association and transplantation PowerPoint Presentation ID9304629
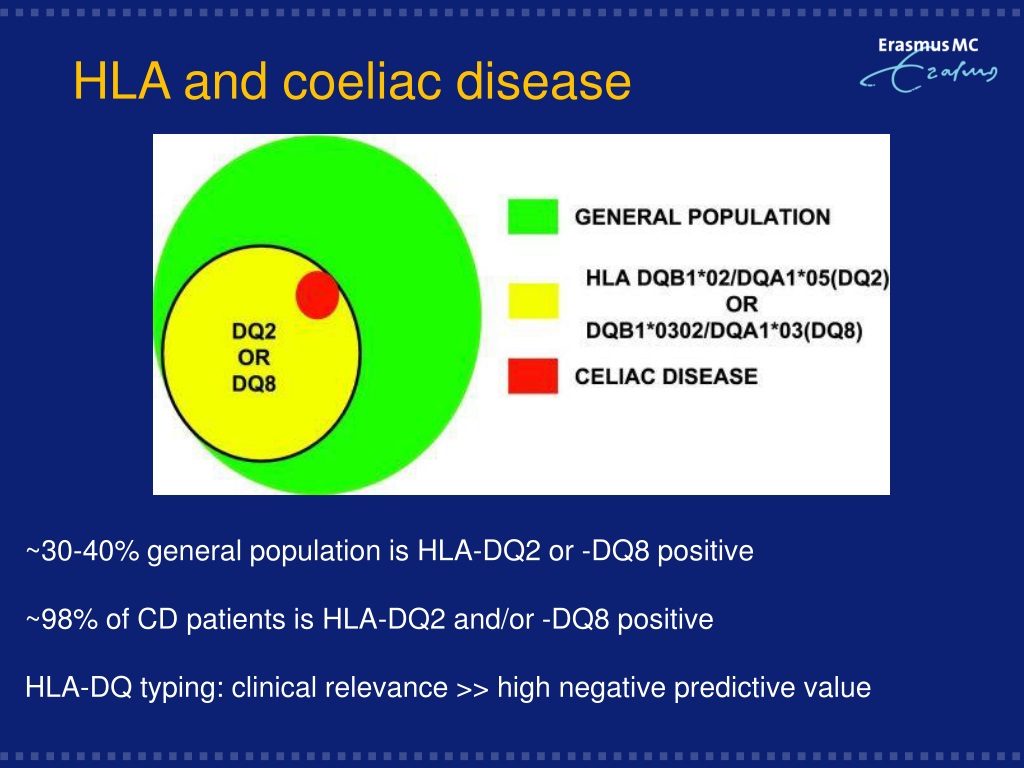
Genetic testing for human leukocyte antigens (HLA-DQ2 and HLA-DQ8) can be used to rule out celiac disease. It's important to be tested for celiac disease before trying a gluten-free diet. Eliminating gluten from your diet might make the results of blood tests appear in the standard range.
(PDF) Human leukocyte antigen (HLA)DQ2 and DQ8 haplotypes in celiac, celiac with type 1

Test Results. Celiac disease is hereditary. This means certain genes put you at risk for developing it. Healthcare providers are increasingly using celiac disease genetic testing to find out if someone is predisposed to developing the condition. Genetic tests for celiac disease look for genes called HLA-DQ2 and HLA-DQ8.
(PDF) High rates of variation in HLADQ2/DQ8 testing for coeliac disease results from an

Genetic testing for HLA-DQ2.5 and HLA-DQ8 may help rule out celiac disease in certain circumstances. For example, health care professionals may order genetic tests in patients for whom other tests do not provide a clear diagnostic result. If a patient's genetic test results are negative for HLA-DQ2.5 and HLA-DQ8, he or she is very unlikely to.
(PDF) The production and crystallization of the human leukocyte antigen class II molecules HLA

The expression HLA-DQ8 can vary significantly from one part of the world to the next. In Europe, for example, it is the most associated with celiac disease and juvenile diabetes. Similarly, in Japan, where this is no HLA-DQ2, the DQ8 serotype is the sole cause of the celiac disease (bolstered, in part, by the influx of gluten in the.
Figure 2 from Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) DQ2/DQ8 prevalence in recurrent pregnancy loss women

Carrying HLA DQ2 and/or DQ8 is not a diagnosis of celiac disease nor does it mean you will ever develop celiac disease. However, if you carry HLA DQ2 and/or DQ8, your risk of developing celiac disease is 3% instead of the general population risk of 1%. Since celiac disease is genetic, this means it runs in families.
test for celiac disease DQ2, DQ8 and half DQ2 Genosalut
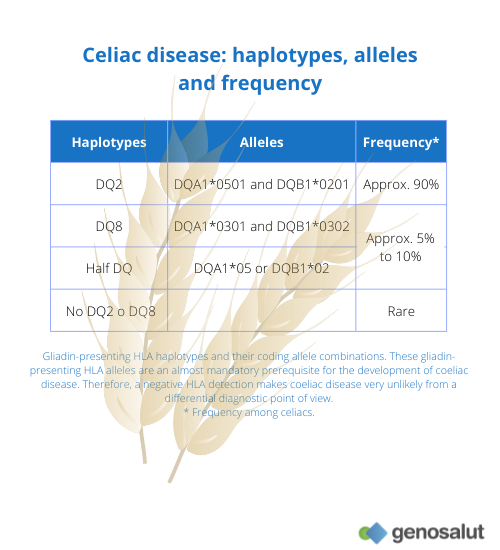
Typing for HLA-DQ2 and DQ8 is considered a useful tool to exclude CD or to make the diagnosis unlikely in the case of a negative test result for both markers. Therefore, ruling out the expression of DQA1*05 , DQB1*02 and DQB1*03:02 is of critical importance for the exclusion of CD in suspected patients.
Rapid Detection of the Three Celiac Disease Risk Genotypes HLADQ2.2, HLADQ2.5, and HLADQ8 by

It has been emphasised that a negative result of HLA-DQ2/DQ8 test excludes CD in 99% and a positive result points to the disease or to a predisposition to it [1, 16]. The performance of genetic testing is indicated to recognise or exclude CD in patients with ambiguous or contradictory results of serological and histopathological investigations.
hla dq2 hla dq2 dq8 maladie coeliaque Genertore2

By definition, HLA (human leukocyte antigen) is a cellular protein that triggers an immune response. With celiac disease, aberrations in the HLA coding can cause the immune system to go haywire in the presence of gluten and attack cells of the small intestine. Despite the fact that HLA-DQ2 and HLA-DQ8 are both linked to this effect, having the.
(PDF) HLADQ2 and DQ8 genotype frequency in Syrian celiac disease children HLADQ relative

Celiac disease is a common inflammatory disease triggered by dietary gluten in genetically susceptible individuals. The strongest and best-characterized genetic susceptibilities in celiac disease are class II human leukocyte antigen (HLA) genes known as HLA-DQ2 and DQ8. HLA genetic testing is available through a number of commercial and.
GlutenSpecific T Cells CrossReact between HLADQ8 and the HLADQ2α/DQ8β Transdimer The

HLA-DQ2 and DQ8 are found to play important roles in the development of celiac disease.HLA-DQ2 and DQ8 can uniquely present specific gluten-derived peptides, compared with other HLA types that cannot. Inflammation is triggered by a pathogenic process in which antigen-presenting cells present deamidated gluten that binds to HLA-DQ2 or DQ8.However, this pathogenic process is inactive in most.
(PDF) Rapid detection of the three celiac disease risk genotypes HLADQ2.2, HLADQ2.5, and HLA
HLA testing can also be useful when serology and histology conflict because a negative test result for HLA DQ2 and DQ8 rules out celiac disease. Implementing a Gluten-Free Diet.
Celiac Facts for Patients Lesson 2 Why Some People Get Celiac Disease and Others Don't

The HLA class II antigens DQ2 (DQA1*05/DQB1*02) and DQ8 (DQA1*0301/DQB1*0302) are the major risk factors predisposing individuals to Celiac Disease and account for over 35% of the genetic risk. Close to 90% of patients with Celiac Disease express the HLA-DQ2 molecules with most of the remainder expressing the HLA-DQ8 molecule.
.